Tags
Reliability, Availability and Serviceability (RAS) are related to a products ability to deliver its intended functionality. Essentially how long and how well.
Definitions
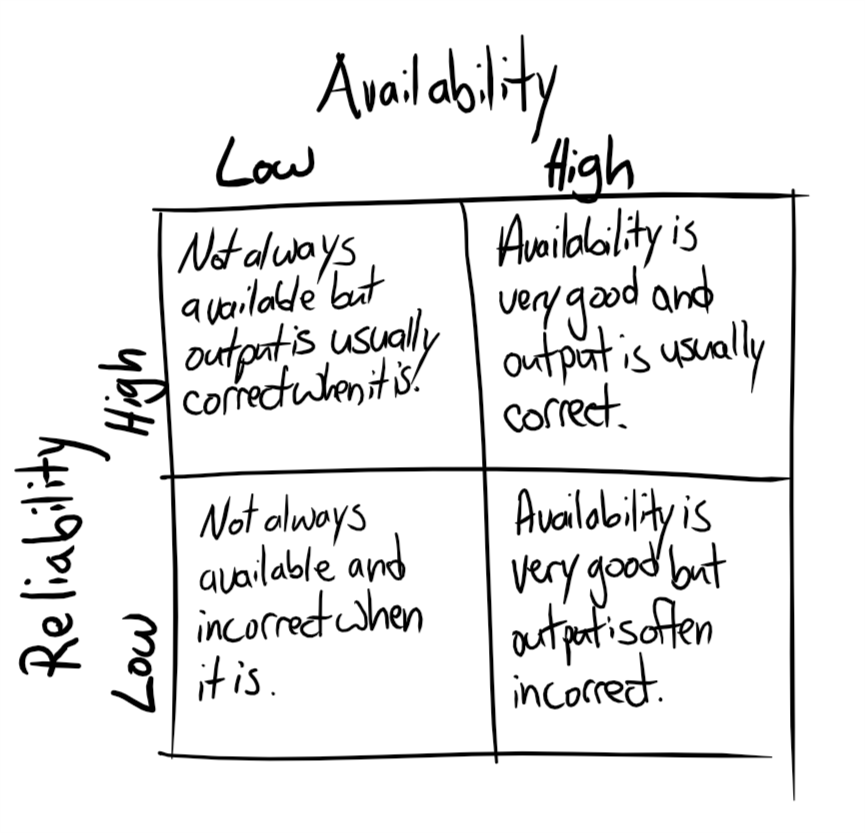
Reliability: is the ability (i.e. probability) of a device to provide correct outputs, given a specific operating environment.
Availability: is the likelihood (i.e. probability) of a device to be available for usage at a given time.
Serviceability: is the efficacy of a device to be repaired.
 Design Guidelines
Design Guidelines
- Identify Flows
- Map flow of device outputs (e.g. functions)
- Identify all failure modes along flow
- Identify single point failures
- Determine or calculate expected time between failures on a per component and per system level
- Component lifespan
- Component aging
- Derate components for sufficient margin
- Mitigation
- Implement redundancy as needed
- Implement high reliability hw as needed
- Detection
- Sampling of output
- Injection
- Monitoring hardware (e.g. self detection)
- Diagnostics
- Alerting and reporting failures
- Recovery and Repair
- Can the user accept reduced capacity (e.g. run slower, wider error, etc)?
- Automated failover
- Service (online)
- Service (offline)
- Repeat at all levels of the stack (memory is used as an example)
- Memory cell
- Memory row
- Memory silicon and packaging
- Memory PCB
- Memory controller or CPU
- Memory bus
- OS memory manager
- OS process manager
- Process
Resources
Reliability engineering
Availability
- Log in to post comments